Research Provides a Deeper Understanding of Salicylic Acid-Induced Anthracnose Resistance
The fungal pathogen Colletotrichum sublineolum (C. sublineolum) causes the devastating disease anthracnose in sorghum, an important cereal crop which feeds 500 million people in Africa and Asia, and is also used for forage, animal feed, and biofuel production. C. sublineolum infections can cause crop losses as high as 86 percent. Anthracnose resistance in sorghum would reduce the need for non-environmentally friendly fungicide use and substantially decrease losses; research into the mechanisms behind such resistance is of great interest to scientists, growers and breeders.
In an effort to determine the role of salicylic acid (SA) in sorghum resistance to anthracnose, researchers from Shandong University in China studied the effect of exogenous SA on resistance in the sorghum lines BTx623 and WHEATLAND. The scientists discovered that exposure to C. sublineolum enhanced SA-responsive gene expression, and when SA was exogenously introduced to the BTx623 sorghum line, resistance to anthracnose increased. To determine if this effect was due to the toxicity of SA to C. sublineolum or to a molecular mechanism within the plant, WHEATLAND, an SA-tolerant line was also exposed to an SA treatment. The SA treatment did not result in anthracnose resistance in the WHEATLAND line supporting the idea that the exposure resulted in a response within the BTx623 plants that led to anthracnose resistance.
The transcriptomic mechanisms for SA-induced anthracnose resistance in both SA-sensitive and SA-tolerant lines were evaluated using RNA-seq. Two pathways, the cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis pathway, which is involved in the plant immune response, and the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, which is involved in anthracnose resistance, were enriched in BTx623-specifically upregulated genes. In addition, several immune-related genes were differentially expressed in BTx623 and WHEATLAND, including orthologs of WRKY70 and cysteine protease, both of which are known to regulate SA signaling and/or plant immune responses.
SorghumBase example:
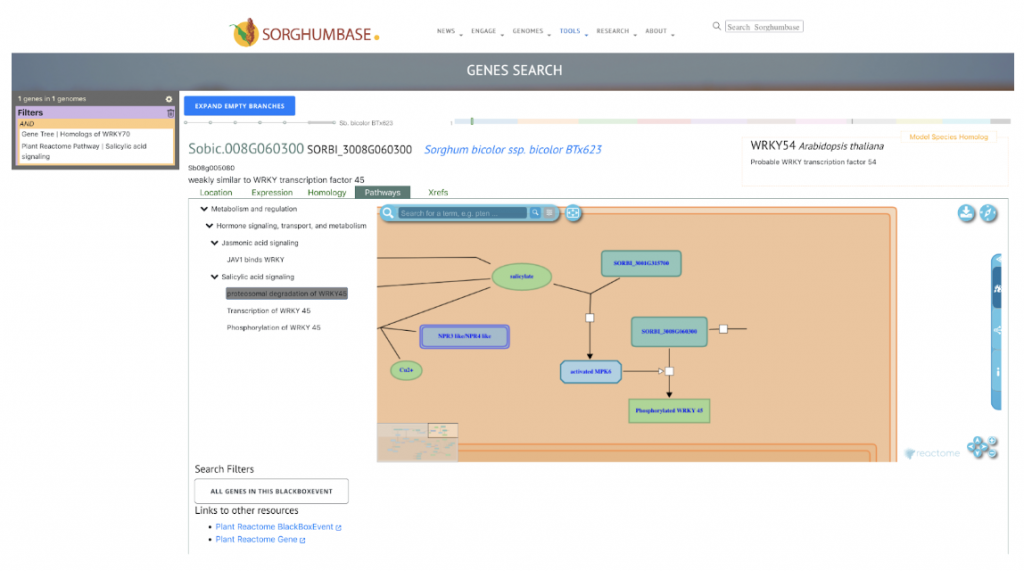
Reference
Sun X, Li A, Ma G, Zhao S, Liu L. Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the bases of salicylic acid-induced resistance to anthracnose in sorghum. Plant Mol Biol. 2022 Jul 6. PMID: 35793006. DOI: 10.1007/s11103-022-01286-5. Read more
Related Project Website:
Lijing Liu, Shandong University https://www.lifesci.sdu.edu.cn/enj/info/1086/1539.htm


